Financial Statement
Financial statement or Final accounts are statements use to
conveying the profitability and financial position of the business to
management, owners and interested outsiders. It is the end process of
accounting which gives clear and brief accounting information of a particular
accounting year after the period is over. Generally financial statements
contain two parts:
1. Income statement
2. Balance Sheet
INCOME
STATEMENT:
Income statement is prepared to ascertain the
profitability position of the business. Income statement is divided into two
sections:
A.
Trading Account
B.
Profit and Loss Account
A.
Trading Account
Trading account is prepared to ascertain the
trading results of a business. This means how much Gross profit/loss the
business has earned from buying and selling during a particular period. The difference
between the sales and cost of goods sold is Gross profit/loss, i.e.
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold.
Net Sales = Sales – Sales Return.
Cost of
Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Net Purchases +
Direct Expenses – Closing Stock.
Net Purchases = Purchases – Purchases Returns
Direct Expenses
All those expenses which
have been incurred in purchasing the goods (raw materials), bringing them to
the business premises and make them fit for sales.
Generally following are
the direct expenses:
Carriage inwards,
Cartage , Royalty, Freight, wages, Customs duty, Import duty, Dock duty,
Octroi, Electricity, Water, Fuel, Power, Primary packing materials, Factory cleaning,
Consumable stores ( cotton waste, Grease, Engine oil, Soft soap etc.), Factory
expenses ( Factory rent, factory insurance, factory lighting and factory
heating).
Trading results can
also be ascertained by using an accounting form as follows:
Trading Account for the year ended………………………….

B. Profit
and Loss Account
Profit and loss account is an extension of
trading account. This account is prepared to calculate the net profit of the
business. This account begins with the Gross profit/loss b/d from the trading
account.All the indirect expenses like Selling
and Distribution expenses, Management expenses, Depreciation and maintenance,
Financial expenses and Extra ordinary expenses are debited in this account.
This account is credited with all the Incomes
and Gains other than sales.
Following is a proforma of Profit and Loss
Account:
Profit
and Loss Account
for the year ended............
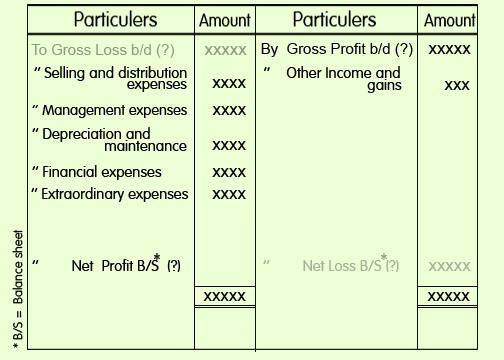
1. Selling and
distribution Expenses:
This expenses includes Advertisement, Traveller’s salaries, expenses
and commission, Bad debts, Godown rent, Export expenses, Carriage outwards, Bank
charges, Agent’s commission,Up keeping of motor lorries,etc.
2. Management
Expenses:
This expenses includes Rent, rates and taxes, Heating and
lighting, Office salaries, Printing and stationary, Postage and telegrams,
Telephone charges, Legal expenses, Audit fees, Insurance, General expenses,
etc.
3. Depreciation and
Maintenance:
This expenses includes Depreciation of various assets,
repairs and maintenance.
4. Financial
Expenses:
This expenses includes discount allowed, Interest on
capital, Interest on loans, Discount on bills discounted, etc.
5. Extraordinary
Expenses:
This expense includes loss by fire not recovered by
insurance, etc.
6. Other Incomes and
Gains:
This item includes Interest received, Discount received, Commission received, Rent received, Income from investment, Bad debts recovered,Income from any other sources, Miscellaneous revenue receipts etc.
BALANCE
SHEET:
A Balance
Sheet is a statement prepared with a view to measure the financial position of
a business on a certain fixed date. It is also described as a ‘Statement
showing the sources and application of capital”. It is a statement and not an account and
prepared by using the balancing figures in the Assets , Liabilities and Capital accounts.
Balance
sheet has two parts. On the left hand side Liabilities and Capital are recorded
and on the right hand side all the assets are recorded.
Marshalling
of Assets and Liabilities
The
arrangements of assets and liabilities in certain groups and in a praticular
order is called grouping and marshalling of assets anf liabilities. We can
arrange assets and liabilities in the balancesheet in two ways.
i. In the order of liquidity
ii. In the order of permanence
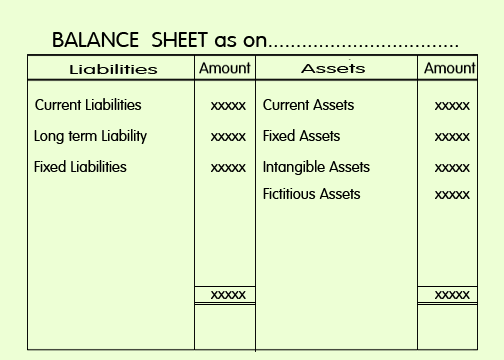
i. In the order of liquidity
When
assets and liabilities are arranged according to their realizability and
payment preferences, such an order is called liquidity order.
Following is an example for the arrangement of balance sheet in the order of liquidity:
ii. In the order of permanence
When the
order of reversed from that what is followed in case of liquidity is called
order of permanence. This order is compulsory for companies.
Following is an example for the arrangement of balance sheet in the order of permanence:

1. Out standing Expenses
2. Pre paid Expenses 3. Out standing Income 4. Income received in advance 5. Depreciation 6. Interest on Capital 7. Interest on Drawings | 8. Bad debts
9. Provision for bad and doubtful debts 10. Provision for discount on debtors 11. Defered Revenue Expenditure 12. Loss of good by fire |